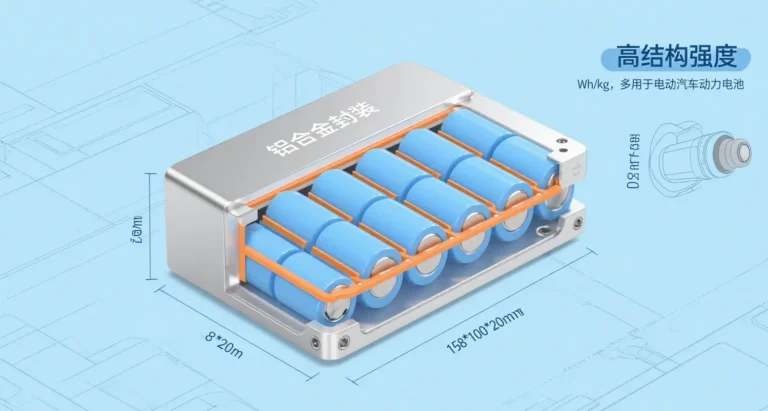
Ultra-low temperature and high capacity lithium battery technology
The six-rotor UAV of Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, flies stably in the cold night of -36℃ in Mohe; the ultra-low-temperature battery of Xingdong Li-ion battery has a discharge retention rate of 95.37% in the environment of -35℃ – in 2025, China is reshaping the global competition pattern of ultra-low-temperature, high-capacity lithium batteries with material innovation and standard definition.
1、Technological breakthrough: China’s ultra-low temperature high-capacity lithium battery program to conquer the extreme cold environment
Electrolyte formulation innovation has become the core breakthrough of ultra-low temperature battery. Chen Zhongwei team of Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, developed a mixed solvent of fluorinated ethylene carbonate (FEC) and methyl decanoate, which lowers the freezing point of the electrolyte to -75 ℃, and at the same time inhibits the low-temperature expansion through the elastic buffer layer on the surface of the silicon-carbon negative electrode, so that the battery in the -40 ℃ environment, the range of the attenuation rate of less than 10% of the ambient temperature, which is far lower than the industry’s attenuation level of 30% -50%. The six-rotor UAV equipped with this battery successfully completed complex path cruising at -36℃ in Mohe, with smooth voltage output and no power fluctuation.
Semi-solid state battery system synchronized to overcome the contradiction between safety and performance. Through the innovation of in-situ gel electrolyte and stacking process, Xingdong Li-power has constructed an ultra-wide temperature range working capability (-35℃ to 65℃), with a high discharge capacity retention rate of 95.37% under the extreme environment of -35℃, and without the need of external heating system. The battery pack has passed the 95-type rifle gunshot test, and there is no fire or explosion under fully charged state, and the safety performance reaches the military level.
Solid-state batteries have made milestone progress in low-temperature adaptability. The cycle life of the 400Wh/kg lithium metal anode battery developed by Ganfeng Lithium exceeds 800 times, while the silicon-based anode system realizes a gradient layout of 320-450Wh/kg, and the energy density of the 21700 cylindrical battery core covers 330-400Wh/kg, which provides polar drones and robots with a power solution that combines high energy density and low-temperature stability.
Material Innovation: Reconstruction of Ion Transmission Paths
Anode materials’ low-temperature performance jumps up
Lithium Source Technology’s world-first T246 low-temperature, high-magnification cathode material significantly optimizes the lithium ion transport path through precursor nanosizing and bulk phase doping processes:
-20℃ capacity retention rate of more than 60%, powder compaction density>2.40g/cm³, balancing low-temperature performance and energy density
1C charging and discharging capacity of more than 160mAh/g, up 7.6% compared with traditional products, to meet the demand for instantaneous high-horsepower output of heavy-duty trucks.
Negative electrode interface dynamics optimization
The porous composite collector jointly developed by Harbin Institute of Technology and State Grid Heilongjiang Power breaks through the limitations of traditional metal collectors:
The porous polymer substrate is plated with aluminum/copper layers on both sides, which can store electrolyte and provide an ion source.
achieves a 30% increase in high-current discharge capacity at -40°C, while alleviating the problem of electrolyte drying out and prolonging the life of the battery.
The black phosphorus (BP)-Mo/Sn₂P₂O₇ composite anode designed by a Chinese research team maintains a high capacity of 616mAh/g at -50°C, with a capacity retention rate of 92% after 175 cycles. The core of the composite anode is that Sn₂P₂O₇ acts as an “active Li⁺ reservoir” to dynamically regulate the interfacial ionic concentration, and induces the formation of a Li₃P-based SEI membrane with a 100-fold increase in ionic conductivity.

3、 Ultra-low temperature and high capacity lithium battery application scenarios: from polar scientific research to low-altitude economy
Extreme Environment Operation
Polar scientific research: CAS ultra-low-temperature batteries support UAVs to travel over 200 kilometers in a single trip, solving the problems of polar material delivery and data collection.
Disaster rescue: Xingdong lithium battery packs start up instantly without preheating at -35℃, guaranteeing the rescue equipment to run continuously for 12 hours in a blizzard environment.
Transportation Revolution
Electrification of heavy trucks: T246 material enables lithium iron phosphate batteries to maintain more than 60% capacity at -20°C, solving the pain point of winter range shrinkage of logistics trucks in cold areas
Aerospace: Ganfeng Lithium’s 400Wh/kg solid-state batteries are adapted to the eVTOL aircraft, and the samples have entered into the airworthiness certification process
Consumer Electronics and Specialty Equipment
Smartphone: Ganfeng Lithium’s low-temperature-resistant solid-state batteries send samples in bulk to international head cell phone companies, solving users’ range anxiety in cold regions
Military Equipment: Xingdong Battery Passes Type 95 Rifle Gunshot Test, Provides Stable Power Supply at -40℃ for Border Patrol Equipment
4、Competition in the industry chain: Chinese enterprises’ global layout
Competition for the right to define technical standards
China takes the lead in promoting the internationalization of ultra-low-temperature battery test specification, and the index of “-40℃ cycling capacity retention rate>90%” proposed by Xingdong Li-power has become the industry benchmark.5 The “All-solid-state Battery Determination Methods” (2025) requires that the weight loss rate is <1% after drying at 120℃ for 6 hours, which establishes authoritative yardstick for the industry.
Technical route of leading enterprises
| corporations | technological route | Core indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Xingdong Lithium | In situ gel semisolid batteries | -35℃ discharge retention rate of 95.37% |
| Ganfeng Lithium | Lithium metal negative solid state batteries | 400Wh/kg energy density, 800 cycles |
| lithium ion technology | T246 Low Temperature Anode Material | -20℃ capacity retention rate 60%, compacted density 2.40g/cm³ |
Deepening of international cooperation: Ganfeng Lithium signed a joint development agreement on solid-state batteries with an international head automobile company; State Grid Heilongjiang Electric Power’s composite fluid collector technology was certified by the European Union’s Clean Energy Organization.

5、Challenges and Future: Industrialization Attack Direction
Current technical bottlenecks
Interfacial impedance: solid-state battery solid-solid interfacial impedance is as high as 80-100Ω-cm², which restricts the fast charging performance
Cost pressure: the cost of fluorine-substituted solvent for ultra-low temperature electrolyte is 3 times of the cost of the conventional system, and the cost of mass production of semi-solid-state batteries is about 1 Yuan/Wh.
Frontier technology breakthrough path
π-conjugated organic materials: Perylene tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride (PTCDA) anode achieves 1.06mAh/cm² surface capacity at -40°C, and electron delocalization effect improves ion transfer efficiency
Localized High Concentration Electrolyte (LHCE): Methyl acetate-based electrolyte supports -50°C discharge and maintains 80.85% of room temperature capacity

Strategic Resource Layout
Closed loop recycling: electrolyte-free characteristics of solid-state batteries reduce recycling pollution by 90%, and the recovery rate of nickel-cobalt-manganese exceeds 95%.8
Sodium resource substitution: Meilian New Material mass-produces Prussian Blue anode materials, easing the pressure on lithium resource dependence on the outside world.
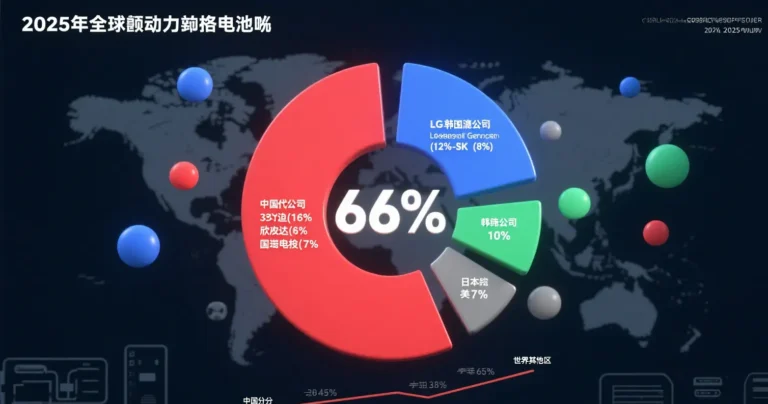
When Xingdong Lithium’s military-grade batteries continue to supply power in snowstorms, and when Lithium Source Technology’s T246 materials drive heavy trucks through the cold zone, ultra-low-temperature lithium batteries have evolved from a technological concept to a strategic Infrastructure. According to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology forecast, in 2025, the global ultra-low temperature battery market size will exceed 120 billion yuan, China dominates the rule-making with 70% of the core patent share.
In the next five years, the technology evolution will focus on three major directions: solid-solid interface impedance down to below 40Ω-cm² (Jusengan high ALD technology), -50°C ultra-low temperature fast charging system (black phosphorus composite anode), and biodegradable shell (corn starch-based materials). In this energy revolution, the goal of Chinese enterprises is not only to conquer the extreme cold, but also to make high safety, high specific energy lithium technology to become the human exploration of extreme environments “energy passport”.