New Energy Battery Shell Materials and Technology Development in 2025
Battery shell material is not only a protective layer, but also a key component that affects the safety and performance of electric vehicles
With the rapid development of the global new energy automobile industry, the battery pack frame as the core bearing structure of the power battery system, the new energy battery shell material selection directly affects the safety of the vehicle and the range of the battery shell as the battery’s “armor”, not only bears the physical protection function, but also need to meet the lightweight, thermal management, flame retardant and other multiple technical requirements. Management, flame retardant and other multiple technical requirements.

I.The evolution of battery shell materials and technical considerations
The evolution of battery shell materials reflects the pursuit of safety, efficiency and environmental protection in the new energy vehicle industry. From aluminum shell to carbon fiber, from single protection to integrated design, every technological breakthrough is pushing the boundaries of electric vehicles.
Material selection has become a key factor affecting the performance and safety of electric vehicles. With the GB 38031-2025 standard, which will be implemented in 2026, “system level safety” will be included in the mandatory provisions for the first time, which will put forward higher requirements for battery casing materials. The new national standard puts forward more stringent requirements for thermal runaway protection, clearly requiring that no open flame is visible within 24 hours after the loss of control of the battery monomer, and the toxicity of smoke meets the safety standards.
II. The mainstream battery shell materials and their characteristics analysis
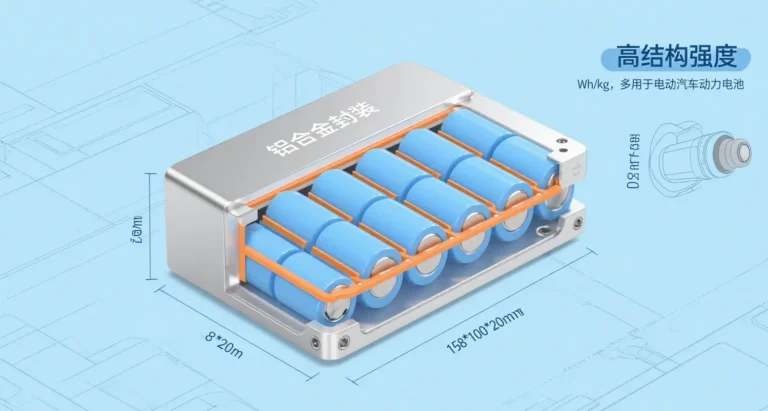
Aluminum alloy material
Aluminum alloy is currently the most widely used battery shell material, mainly made of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy, with the following core advantages:
- Lightweight characteristics: the density is only 2.7g/cm³, 65% lighter than steel, which can significantly reduce the weight of the whole vehicle and improve the range. Measured data show that the battery pack frame with 4040 aluminum profile can reduce weight by more than 30%
- High strength performance: tensile strength up to 310MPa, static load-bearing capacity up to 800kg/m, and deformation of less than 0.3mm under dynamic load, which can effectively protect the battery pack from impact damage.
- Thermal stability: stable performance in the environment from -40℃ to 150℃, and the coefficient of thermal deformation is only 1.2×10 -⁵/°C, better than ordinary carbon steel
- Corrosion resistance: after anodic oxidation treatment (film thickness of 25μm), salt spray resistance time up to 1000-2000 hours, outdoor service life of 15-20 years
Composite material
The application of composite materials in the field of battery shell is accelerating, mainly including the following types:
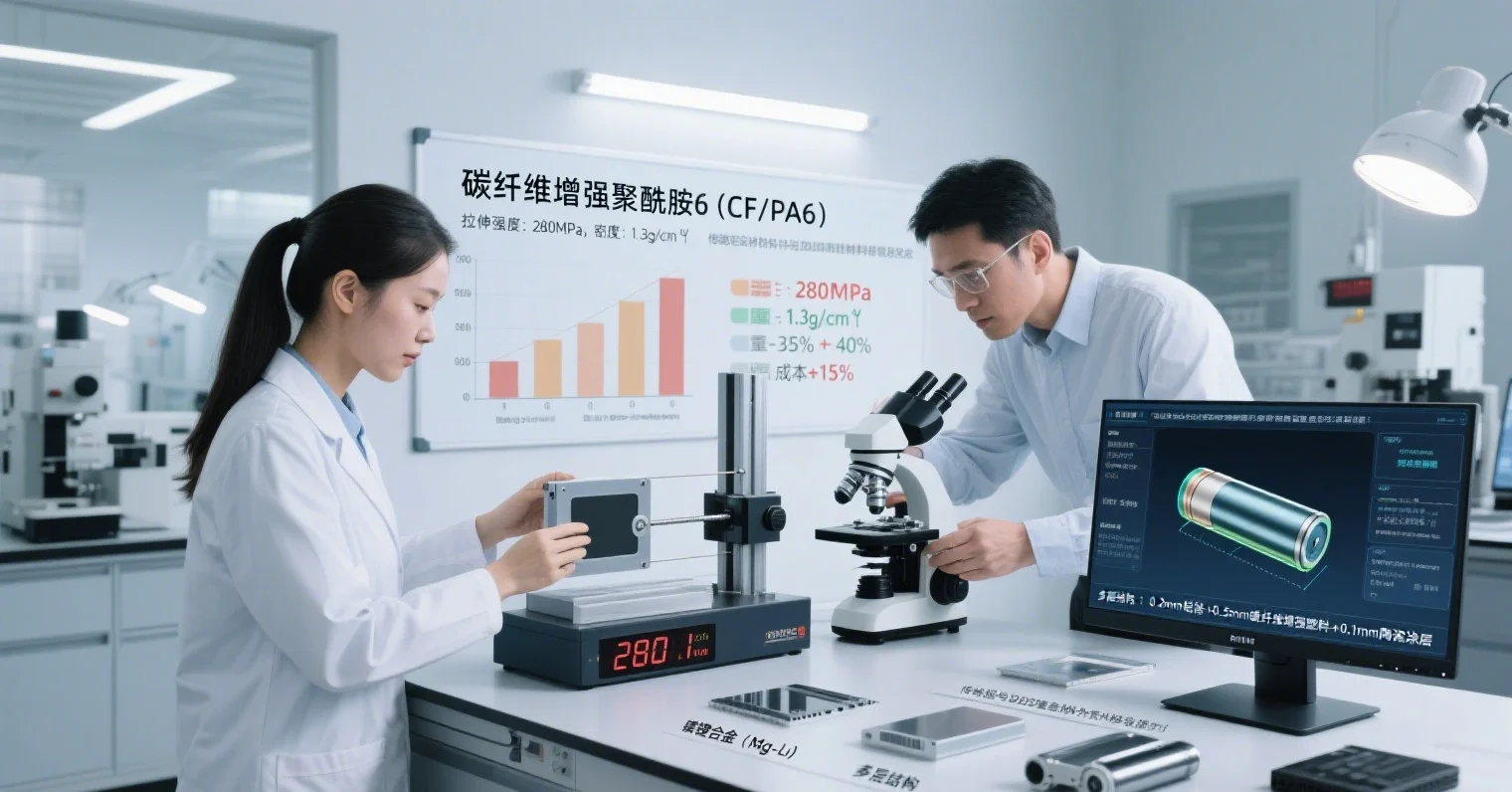
Carbon fiber reinforced composites (CFRP)
Carbon fiber reinforced composites have become the material of choice for power battery shells in high-end models by virtue of their advantages of having a specific strength 5-7 times that of steel and a density that is only 1/4-1/5 that of steel.10 The carbon fiber shells developed by a research institute have a weight reduction of 50% compared to aluminum alloy structures, and their energy density has been increased to 210Wh/kg.
Sheet Molding Compound (SMC)
SMC is a thermoset material with high specific strength (1.7-1.9g/cm³), corrosion resistance, and flame retardancy (V0 grade), which has a significant weight reduction effect in battery cover applications.
Thermoplastic
For example, PA6+GF thermoplastic shells use a single-stage D-LFT molding process, which reduces weight by 40% while integrating collision avoidance structures and thermal management components, and reduces assembly processes by 30%.10 LANXESS and HELLAHUX GROUP of companies have collaborated in the development of the Pocan AF4130 composite material, which is a blend of polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) and acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA) copolymer, containing 30% glass fiber. Blend containing 30% glass fibers and halogenated flame retardants provides significantly low warpage and shrinkage properties, as well as high flame retardancy.
III. Core Performance Requirements of Battery Enclosure
Mechanical performance guarantee
Battery packs are subject to a variety of forces, such as vibration, impact, etc., during vehicle operation. The shell needs sufficient strength and stiffness to withstand these external forces and prevent damage due to collision or bumps, thus ensuring the safety of the battery.
The precise design of the shell morphology is achieved through the application of topology optimization and multi-objective optimization algorithms. Through modal analysis, the resonance frequency of a certain SMC composite upper cover plate is controlled below 120Hz, effectively avoiding vibration fatigue damage; the lower case adopts 8 symmetrically arranged reinforcing brackets together with the design of side impact beams, so that the deformation under the extreme working condition can be controlled within 2mm.
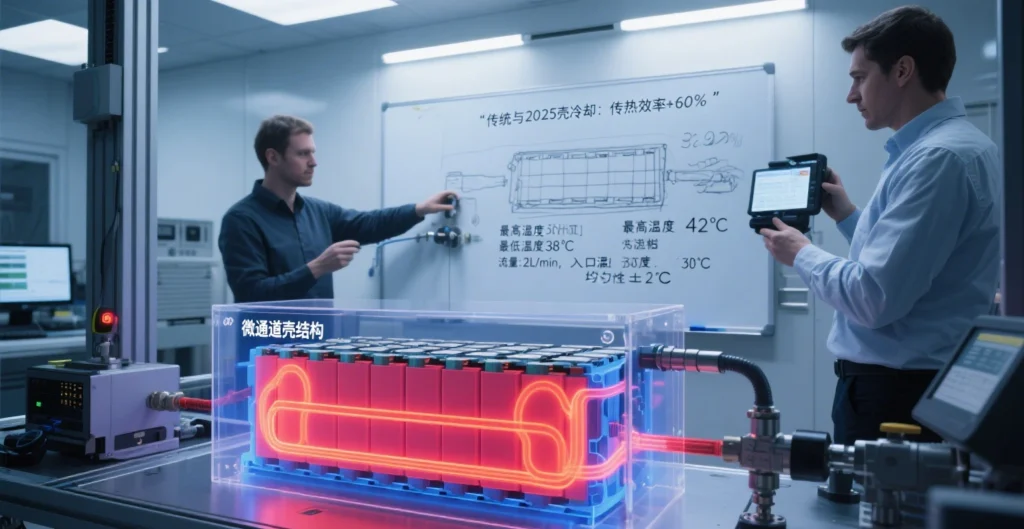
Thermal Management and Flame Retardant Performance
Thermal management and flame retardancy are the key performance indexes of the battery case:
Batteries may overheat or even catch fire during use, and the enclosure needs to have good flame-retardant properties to prevent the fire from spreading and to safeguard the safety of vehicle occupants.7 Some engineering plastics with flame-retardant properties are able to stop the spread of flames for a certain period of time, buying time for evacuation and fire extinguishing.
The new battery casing fire test platform developed by the Aachen Comprehensive Lightweight Manufacturing Center (AZL) combines gradient flame exposure with controlled high-temperature particle impact to simulate thermal runaway scenarios of LFP/NMC batteries, and establishes systematic evaluation criteria for materials in the automotive/aerospace field.2 The test compares the heat resistance and mechanical strength of more than 50 types of materials (metals/plastics/composites, etc.), and evaluates the failure of the materials under flames from 800 to 1200℃. -1200℃ flame failure mode.
Sealing and Corrosion Resistance
Sealing and corrosion resistance are critical to battery enclosures:
Electric vehicles are used in complex and changing environments, and the battery pack shell may come into contact with rain, moisture, chemicals, etc.7 If the shell is not corrosion-resistant, it is prone to rust or erosion, which in turn affects its structural performance and service life7.
Power battery shells need to pass multi-dimensional performance verification: environmental adaptability needs to pass the cold and hot cycle test from -40°C to 85°C and the 1000-hour salt spray corrosion test.10 Stainless steel is a material with good corrosion resistance, which is able to maintain stability in environments with moisture and chemicals.7 In addition, some metals or plastics treated with special coatings are also effective in improving corrosion resistance.7
IV. Innovative Materials and Technology Solutions
Advances in Lightweight Composites
Flame-retardant lightweight composites for new energy equipment are developing rapidly.8 An innovative integrated molding method prepares a lightweight flame-retardant and heat-insulating carbon fiber composite lithium battery pack, which is mainly used in winter scenarios in alpine regions, and has the advantages of lightweight, high impact resistance, and good heat-insulating performance.
This heat-insulating composite battery pack can maintain the optimal working temperature of 20-40°C higher than the outdoor temperature inside the battery pack by only utilizing the heat generated during charging and discharging of the batteries.8 Through the unique design of continuous reinforcement of the core layer, it can realize uniform load transfer and energy dissipation of the lithium battery pack under the impact, vibration, and other force modes, so as to play the best protection effect for the battery cells inside the battery pack.
Intelligent integrated design
The future design of the battery shell is developing in the direction of intelligence and integration:
Multi-physical field coupling simulation technology further improves the design accuracy, through the thermal – force coupling analysis can assess the structural integrity of the thermal runaway scenario, electromagnetic compatibility simulation optimizes the shell shielding layer design, reducing the impact of electromagnetic interference on the battery management system.
The composite shell developed by an enterprise realizes real-time monitoring of collision damage by integrating a sensor network, providing an intelligent solution for the industry.

V. Industry Challenges and Development Trends
Cost Challenges
Although composite shells show significant advantages, their industrialization still faces cost and process challenges:
Carbon fiber raw material price is 8-10 times of steel, need to break the cost bottleneck through material recycling technology. A study shows that the performance retention rate of recycled carbon fiber can reach 85%, but the energy consumption of the recycling process increases by 30% compared with virgin fiber.
Although the hot press tank molding process can ensure the high precision of CFRP shells, its equipment investment accounts for 60%.10 To break the cost bottleneck, the RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) process shortens the molding cycle to less than 2 hours by rapidly curing the resin system, which is more suitable for mass production.
Sustainability Development Trend
Sustainability has become an important direction in the development of battery casing materials:
The industry is exploring alternatives to thermoplastic composites. A PA6+GF thermoplastic shell integrates metal inserts through in-mold injection molding, increasing efficiency by 80% compared to the traditional stamping process.10 A company has adopted regenerated carbon fibers and biobased resins to reduce material costs by 30% while maintaining 90% of the original material’s performance.
As the cost of carbon fiber and thermoplastic composites process matures, composite shells will gradually replace the traditional metal structure to promote new energy vehicle range exceeding 1000 km mark.
VI. Standards and Certification Requirements
Battery cases need to meet a number of strict standards and certification requirements:
- Material standard: meet GB/T3190 composition requirements for 6061-T5 aluminum alloy (silicon 0.2%-0.6%, magnesium 0.45%-0.9%)
- Process standard: anodic oxidation film thickness of GB/T5237.2, building profiles not less than 10μm
- Safety certification: need to be certified by the UN38.3 Transportation Safety Certification and the IATF16949 automotive quality management system. Certification
- Environmental protection requirements: to meet the RoHS directive on the restriction of hazardous substances, lead, mercury and other content shall not exceed the prescribed limits
- Flame retardant certification: need to pass the UL94-V0 flame retardant certification
- Waterproof certification: need to meet the IP67 waterproof certification

VII. Conclusion and outlook
The selection of battery housing materials has become a key factor in the safety, range and overall performance of electric vehicles. From aluminum alloys to carbon fiber composites, various materials are evolving to meet increasingly stringent technical requirements.
With the dual pressures of policy and technology, companies need to seek breakthroughs in the three dimensions of material innovation, structural reengineering, and process optimization.4 By adopting innovative materials such as copper-clad aluminum composites, they can balance the cost and conductivity requirements.4 Or, by using structural reengineering technologies such as the NDT CTB 3.0 technology to replace the traditional aluminum bracket with copper-alloyed beams, they can improve the bottom impact resistance.
In the future, with the popularization of solid-state batteries and intelligent battery management systems, shell materials will usher in a new round of change. The application of composite materials in the field of power battery shells is not only an innovation in material science, but also a change in the design concept of the whole vehicle.10 Through the innovation of the whole chain of material-structure-process-performance, composite shells are becoming a key supporting technology for the lightweighting of electric vehicles, and injecting new kinetic energy into the sustainable development of the industry.