2025 Latest Power Battery Management System (BMS)
As the “intelligent brain” of the battery system, the reliability of BMS directly determines the safety and performance of the power battery.
I. BMS: the control core of power battery system
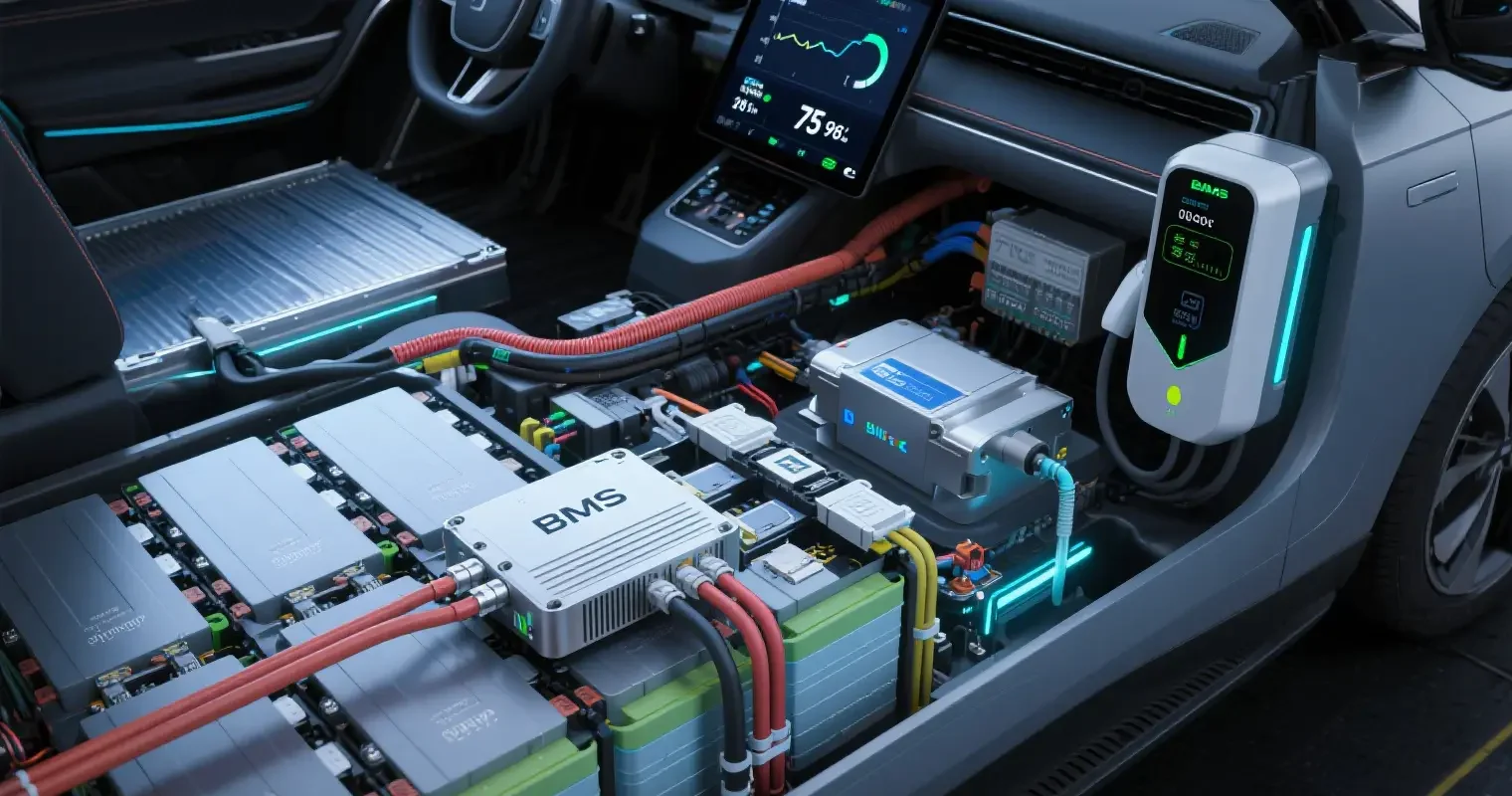
Battery Management System (BMS) is the intelligent control center of the power battery pack, as a crucial part of the battery pack in new energy vehicles, it bears the key responsibility of monitoring, managing and protecting the safe operation of the battery pack. This system ensures the safety and efficiency of the power battery system under various working conditions by monitoring the battery status in real time, preventing abusive operation, prolonging battery life and maintaining optimal performance.
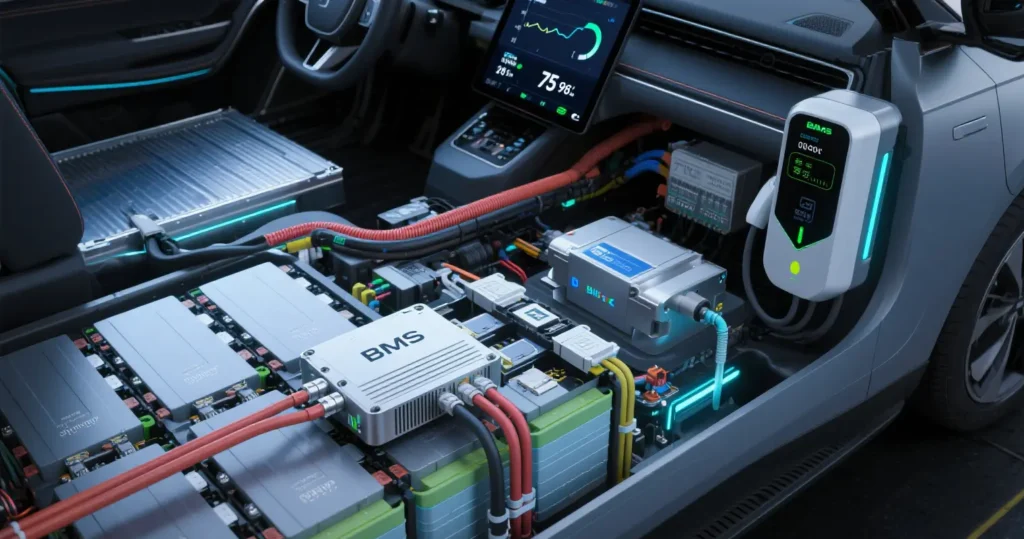

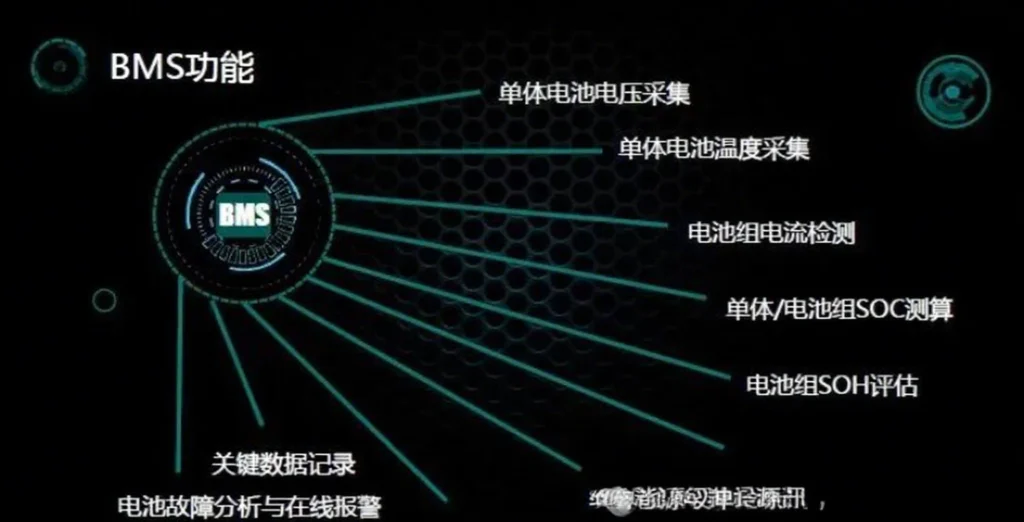
II.Power battery management system BMS core function system
Real-time monitoring function of power battery management system
Power battery management system BMS collects key parameters such as voltage, current and temperature of the battery pack in real time through high-precision sensor network to ensure that the battery pack works in the best condition:
- Voltage monitoring: accurately collect the voltage value of each single cell to detect the consistency of the battery
- Temperature monitoring: monitor the temperature of single cell and coolant to prevent thermal runaway
- Current detection: real-time detection of the battery pack charging and discharging currents, calculation of SOC and SOH
Power battery management system equalization management
Through active or passive equalization technology, the consistency of each cell in the battery pack is maintained to prevent performance degradation caused by differences in battery capacity. Equalization management can effectively improve the overall capacity utilization rate of the battery pack and extend the service life of the battery.
Power Battery Management System Battery State Estimation
SOC (State of Charge) estimation is one of the most important functions of BMS, which directly affects the battery range performance. Highly accurate SOC estimation can maximize the performance of the battery pack, and the error is usually required to be controlled within 5%. Meanwhile, SOH (State of Health) estimation evaluates the health status of the battery and predicts the battery life.
Power Battery Management System Safety Protection Functions
BMS is equipped with multiple protection mechanisms, which can take timely measures when abnormal conditions are detected:
- Over-charging/over-discharging protection: preventing the battery from exceeding the safe voltage range
- Over-current protection: restricting abnormal high-current charging and discharging
- Over-temperature protection: monitoring the temperature and activating the thermal management system
- Insulation monitoring: detecting the insulation condition of the battery system, preventing the risk of electric shock
Power battery management system data communication and storage
BMS records the historical data of battery operation and exchanges data with Vehicle Control Unit (VCU) and charging equipments through CAN bus and other communication interfaces, realizing remote monitoring and management and providing data support for fault diagnosis and maintenance.
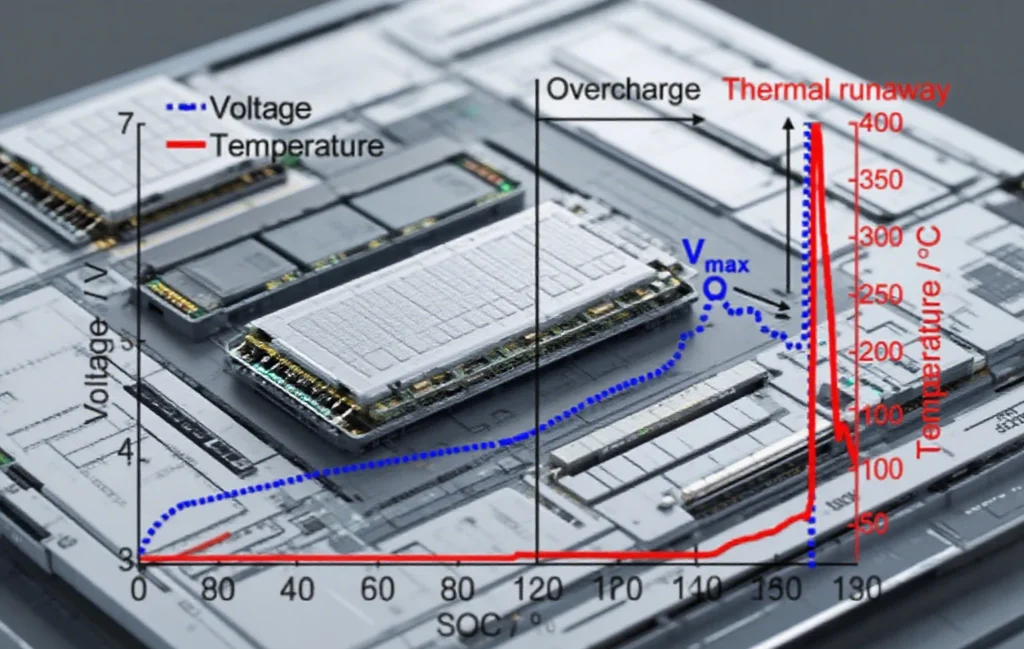
III. Main failure modes of power BMS and their consequences
Voltage detection failure9
Poor connector contact or voltage acquisition line failure leads to the BMS not being able to obtain accurate voltage information, which may cause serious consequences:
- Cannot stop charging in time when overcharging, resulting in battery overcharging
- Cannot cut off the circuit when overdischarging, resulting in battery damage
- Ternary battery overcharging may cause an explosion, and most of the lithium iron phosphate overcharging to more than 5V smoke
Lithium battery overcharging generates heat and gas, firstly, excess lithium is embedded in the negative electrode, which grows lithium dendrites on the surface of the negative electrode; and secondly, excess lithium is dislodged from the positive electrode, which causes the structure of the positive electrode to collapse, and heat and oxygen is discharged. Oxygen is released. Oxygen accelerates the decomposition of the electrolyte, and the internal pressure of the battery continues to rise, which may eventually lead to the opening of the safety valve and the contact of the active substance with air to generate more heat.
Current Detection Failure
Hall sensor failure or current detection circuit abnormality will prevent the BMS from accurately measuring the current value, resulting in:
- SOC calculation deviation increases, affecting the accuracy of range estimation
- Charging current cannot be limited when it is too high, and the internal heat of the battery cell increases
- Temperature exceeding the critical value will cause the diaphragm to solidify and the capacity to decay, which will seriously affect the battery life
Temperature detection failure
Failure of the temperature sensor or acquisition circuit causes the BMS to lose temperature monitoring capability:
- Battery operating temperature is too high, irreversible reaction will occur, affecting capacity and internal resistance
- Cell calendar life is directly related to temperature, the number of cycles at 45℃ is half of that at 25℃
- Battery at high temperature is prone to bulging, leakage, and even explosion problems
- Cannot activate the heating system when charging at low temperatures, which may lead to lithium precipitation and cause short-circuits
Insulation monitoring failure
Insulation failure occurs in the event of deformation or liquid leakage in the power battery system, if the BMS fails to detect it:
- Possible risk of electric shock to personnel
- Increased risk of short circuits and fires
- BMS requires the highest reliability of insulation monitoring sensors
Electromagnetic compatibility issues
Inadequate immunity of the BMS system to electromagnetic interference can result in:
- Communication interruptions or data errors
- Mis-execution or failure of control commands
- Sensor data acquisition anomalies
SOC estimation deviations
The problem of SOC estimation deviation is common to all BMS manufacturers, only the size of the deviation varies:
- In practice, SOC error will become larger and larger, because the use of the environment is more complex
- There are more conditions affecting the accuracy, and the current test standard requires the error to be within 5%
- It is difficult for most manufacturers of BMS to consistently meet this accuracy requirement.
IV. Prevention and Improvement Strategies for BMS Failure
Preventive measures at the design level
- Redundant design: adopt redundant design for key sensors and circuits to improve system reliability
- Electromagnetic compatibility design: enhance anti-jamming capability to prevent communication failure
- Connection reliability: adopt high-reliability connectors to prevent poor contacts
Control of manufacturing process
- Production process control: Strictly control the production process of key components such as voltage collection lines
- Quality testing: Strengthen the factory test to ensure that all functions meet the design requirements
- Aging test: Conduct sufficient environmental stress and aging tests to detect potential defects in advance
Algorithm and Software Optimization
- Multi-model fusion: adopt multiple SOC estimation algorithms to correct each other and improve estimation accuracy
- Machine learning application: optimize the state estimation model by using big data and machine learning algorithms
- Online calibration: develop online parameter identification and calibration algorithms to adapt to changes in battery aging characteristics
V. Industry Development Trends and Challenges
Direction of technological innovation9
- Future BMS technology will develop in the following directions:
- High-precision monitoring: voltage monitoring accuracy of ±1mV, temperature monitoring accuracy of ±0.5°C
- Intelligent prediction: AI-based fault prediction and health management (PHM) technology
- Cloud synergy: cloud BMS and local BMS synergy management to achieve full life cycle optimization
Standardization Challenge
The BMS industry faces the challenge of insufficient standardization:
- Communication protocols: inconsistent communication protocols between different vendors, increasing the difficulty of system integration
- Test specifications: lack of unified reliability testing standards and evaluation system
- Safety certification: safety certification standards and processes need to be improved and enhanced
VI. Application Case: Special Requirements for BMS in Custom Drone Battery Packs
For custom drone battery pack applications, the BMS needs to fulfill special requirements:
- Lightweight design: to achieve full management functions under limited space and weight constraints
- High rate support: to support high rate discharging requirements during UAV takeoff and maneuvering
- Vibration adaptability: to enhance vibration resistance and adapt to the UAV flight environment
- Rapid charging: to optimize the charging algorithm and support off-site rapid replenishment