2025 CATL Power Battery Production Line Analysis
An In-Depth Look at the World’s Leading Power Batteries: CATL Power Battery Production Process and Quality Assurance System
I. Cell Manufacturing: The Core Birth Process of Power Batteries
Mixing Process: Precision Preparation of Active Materials
The mixing process is the first critical step in battery production. It involves uniformly blending solid cathode and anode materials before adding solvents. A vacuum mixer then stirs the mixture into a consistent slurry. Quality control in this stage directly impacts the final battery quality and product yield rate.
CATL’s mixing workshop maintains pharmaceutical-grade dust control standards, ensuring precise control over raw material ratios, mixing steps, and stirring duration to prevent dust from adversely affecting battery consistency.
Coating Process: Core Technology for Electrode Sheet Formation
The uniformly mixed active materials are coated at 80 meters per minute onto both sides of a 4,000-meter-long copper foil. Prior to coating, the copper foil measures a mere 6 microns thick—as thin as a cicada’s wing.
The coating process must guarantee consistent electrode thickness and weight while preventing contamination by particles, debris, or dust. Any deviation may cause accelerated battery self-discharge or even safety hazards.
Cold Pressing and Pre-Slitting: Key to Boosting Energy Density
The cold pressing process uses rollers to compact the coated electrode sheet to the predetermined thickness and density, enhancing energy density while ensuring thickness consistency. Pre-slitting follows, cutting the sheet to the required battery dimensions with strict control over burr formation to prevent safety hazards from burrs piercing the separator.
Battery Tab Die-Cutting and Slitting: Forming the Battery’s “Ears”
The tab die-cutting process uses a die-cutting machine to form the conductive tabs—the connection points for the battery’s positive and negative electrodes during charging and discharging. The slitting process uses a cutting blade to divide the battery electrode sheet, preparing it for subsequent winding operations.
Cell Winding Process: Shaping the Cell Prototype
The positive electrode sheet, negative electrode sheet, and separator are combined through winding to form the bare cell. CATL employs advanced CCD vision inspection equipment for automated detection and alignment correction, ensuring precise sheet positioning with automation levels reaching international leadership.

Baking and Electrolyte Filling: Infusing the Cell’s “Blood”
The baking process removes moisture from the battery interior, ensuring optimal performance throughout its lifecycle. The electrolyte filling process involves injecting electrolyte into the baked cell. This electrolyte acts like blood flowing through the cell, enabling charged ions to complete energy exchange.
Electrolyte volume requires precise control—excess can cause overheating or failure, while insufficient amounts impair cycle performance.

Formation Process: Activating the Cell
Formation activates the cell post-electrolyte filling. Through repeated charging and discharging, it triggers internal chemical reactions that form the SEI (Solid Electrolyte Interphase) film. This ensures the cell’s safety, reliability, and extended cycle life during subsequent charging and discharging cycles.
The cell then undergoes a series of rigorous “health checks,” including X-ray inspection, solder joint quality testing, insulation testing, and capacity testing.
II. Module Assembly: From Individual Cells to System Integration
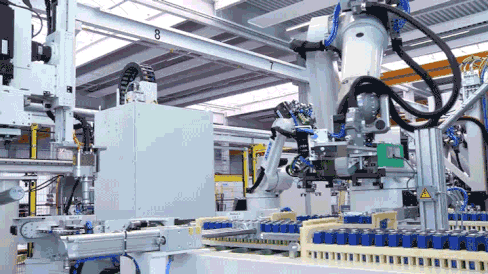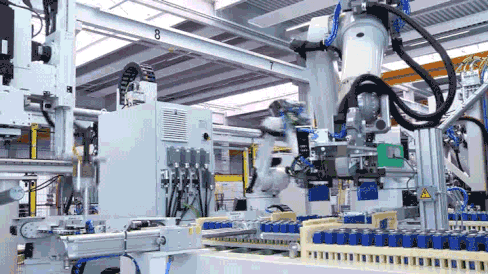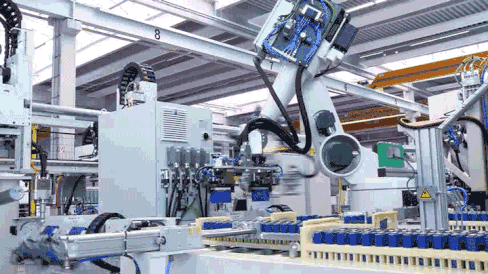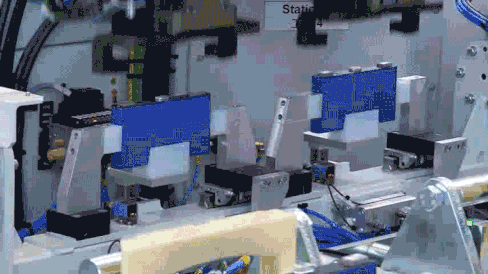
Feeding and Plasma Cleaning
During module assembly, cells are first transported to designated positions where robotic arms automatically pick them up and feed them into the module assembly line. CATL employs plasma cleaning technology to thoroughly clean the surface of each cell, ensuring no contaminants adhere to the cell base during production.
Plasma cleaning represents the most thorough stripping method among cleaning techniques. Its key advantages include zero waste liquid post-cleaning and the ability to clean both entire surfaces and specific areas of complex structures across various materials.
Cell Adhesive Application and Fixing
Before assembly, cells require surface adhesive application. This adhesive not only secures the cells but also provides insulation and heat dissipation functions. CATL employs internationally advanced high-precision adhesive application equipment integrated with robotic arms. This system applies adhesive along preset trajectories while continuously monitoring application quality, ensuring consistency across different battery module assemblies.
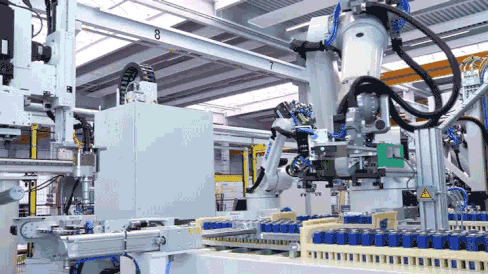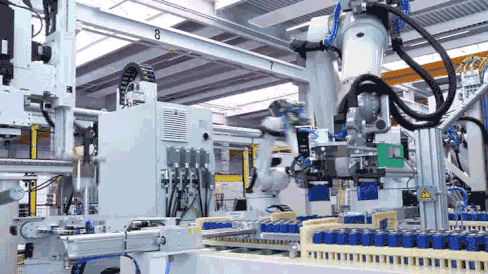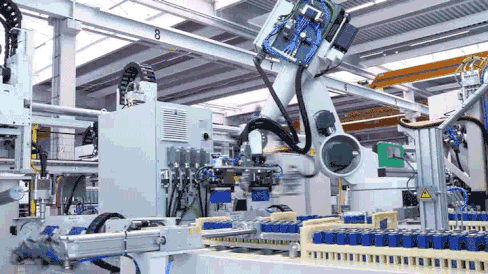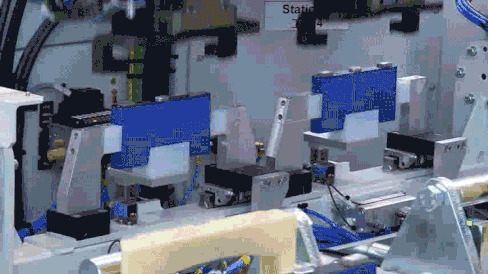
Structural Component Welding and Harness Installation
Battery modules are primarily constructed by welding aluminum end plates and side plates, processed through robotic lamination and welding. After the welding monitoring system precisely locates the welding position, the wiring harness separator material barcode is bound to the MES production scheduling management system, generating a unique code for traceability.
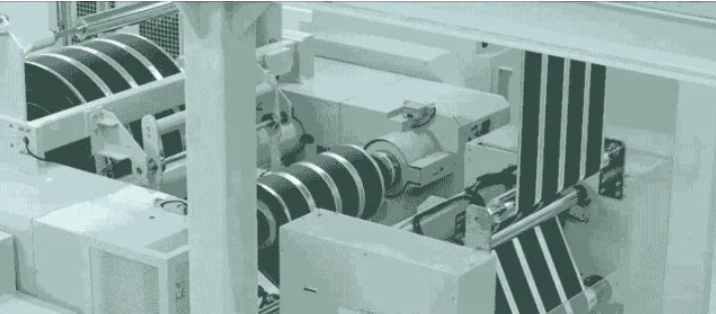
Laser Welding and Final Testing
Automatic laser welding connects the terminals and busbars, enabling series and parallel connections within the battery. Before final assembly, modules undergo comprehensive performance testing, including module voltage/resistance, individual cell voltage, withstand voltage testing, and insulation resistance testing.
III. Quality Testing: Reliability Validation in Extreme Environments
Fire Test: High-Temperature Limit Challenge
CATL conducts fire tests at 590°C, far exceeding the national standard requirement of 130 seconds for external combustion testing. Even under such extreme temperatures (exceeding the melting points of metals like lead and zinc), the battery pack must remain free from ignition or explosion, ensuring no secondary damage occurs even if the vehicle catches fire.

Vibration Testing: Simulating Driving Fatigue
CATL employs a 20-ton thrust vibration table to replicate the bumpy road conditions encountered by battery packs during actual use. The battery pack must undergo continuous random vibration for 21 hours under environmental conditions ranging from -30°C to 60°C, simulating the fatigue equivalent of hundreds of thousands of kilometers of driving.
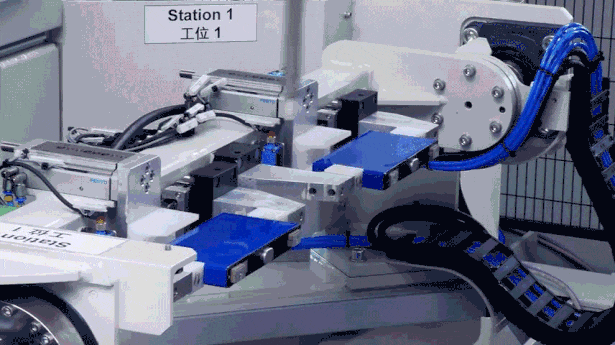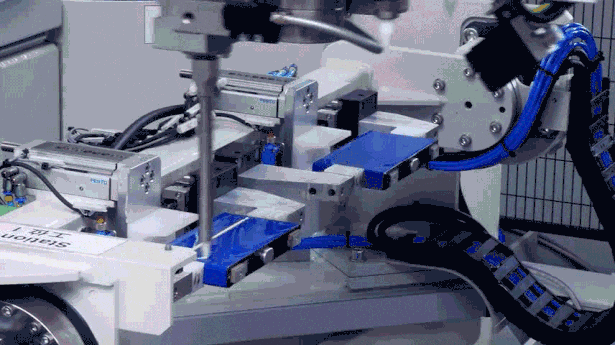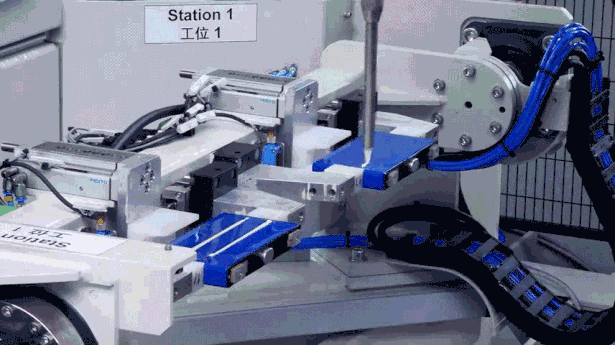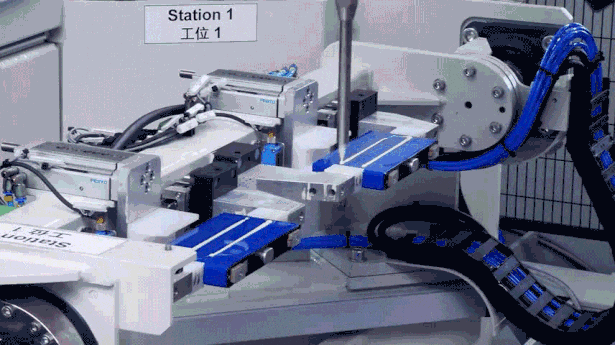
Impact Test: Acceleration Limit Challenge
Impact testing simulates the structural shock to the battery pack from sudden jolts when a vehicle hits road obstacles. CATL’s impact test reaches peak accelerations of up to 100G (equivalent to over six times the centripetal acceleration of a manned spacecraft), ensuring the battery pack functions normally under extreme impacts.
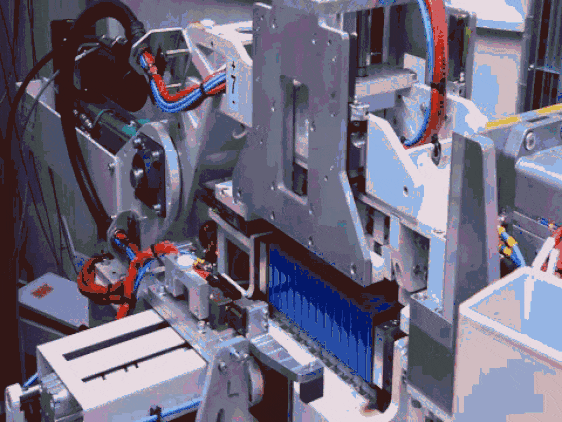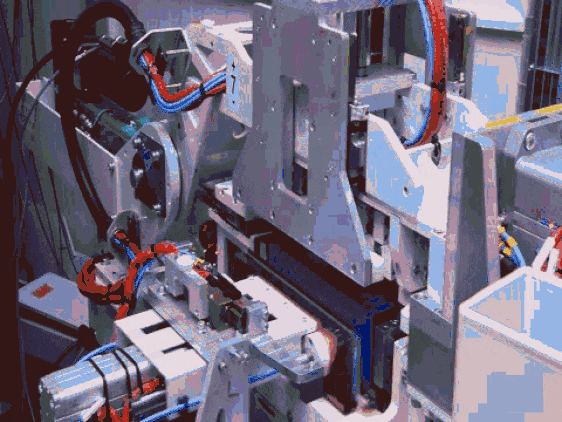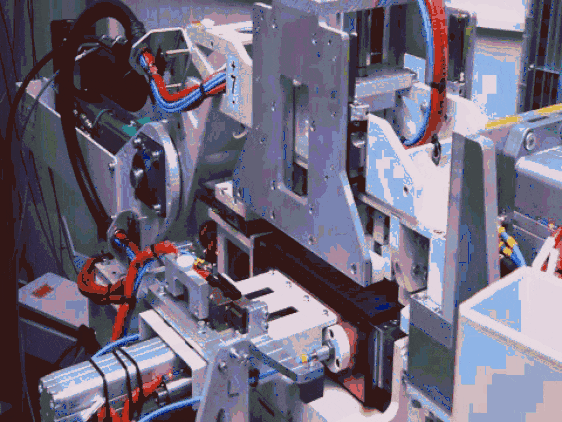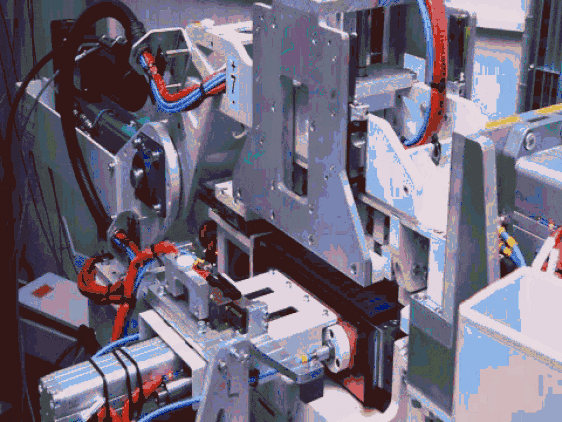
Crush Test: Simulating Traffic Collisions
Crush tests simulate the compression forces a battery pack endures during traffic accidents. CATL’s crush test subjects the battery pack to a 10-ton force, replicating the impact pressure from a 12-meter bus collision (vehicle weight approx. 7 tons, reaching nearly 10 tons with passengers and luggage). Even when severely deformed under compression, the battery pack must continue functioning normally without igniting or exploding.
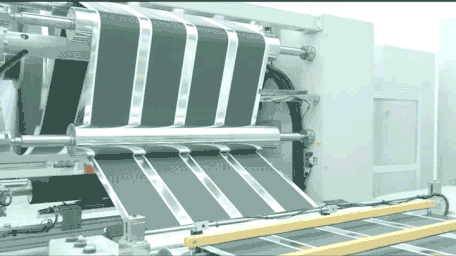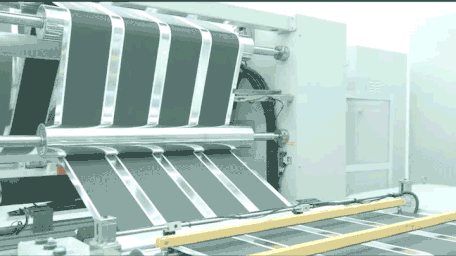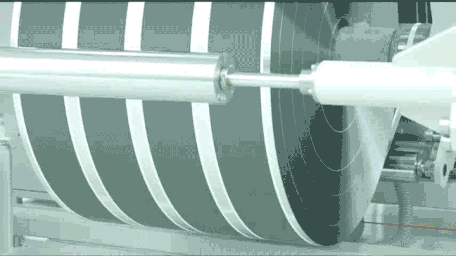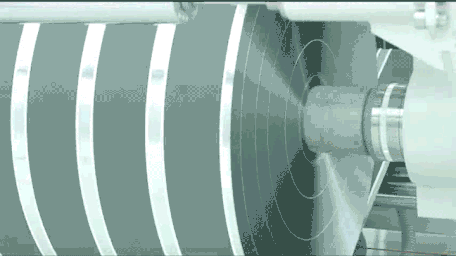
IV. 4680 Large Cylindrical Batteries: Future Technology Direction
For customers interested in customizing lithium-ion 4680 batteries, understanding the new production processes for 4680 batteries is essential. Compared to traditional cylindrical batteries, the 4680 production flow primarily adds new steps such as tab die-cutting, tab flattening, and current collector welding, while also imposing higher demands on casing production equipment.
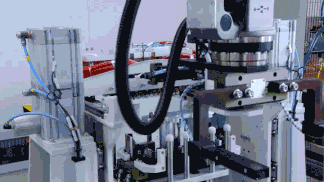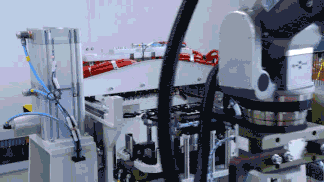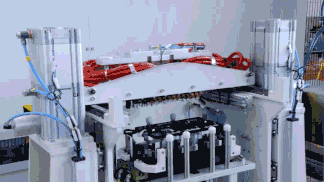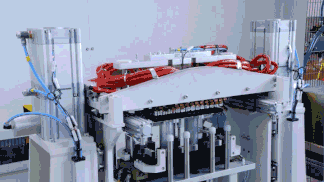
CATL has achieved breakthroughs in tab flattening technology, filing an international patent application for “Tab Flattening Device, Tab Flattening Control Method, and Battery Production System.” This demonstrates the company’s R&D investment and progress in key 4680 battery technologies.

V. Smart Manufacturing and Quality Traceability
CATL’s production lines achieve high levels of automation and intelligence, with 100% automation from material handling to equipment feeding. Each individual cell and module carries a unique QR code recording information such as manufacturing date, production environment, and performance parameters. A robust traceability system documents all relevant data, enabling immediate retrieval of production records during anomalies to support subsequent design improvements.
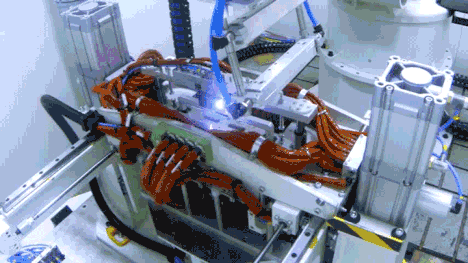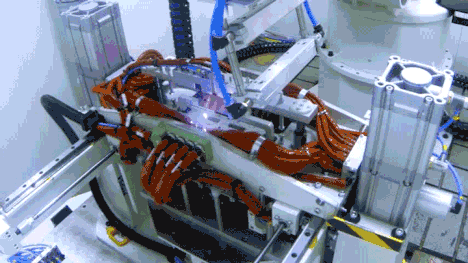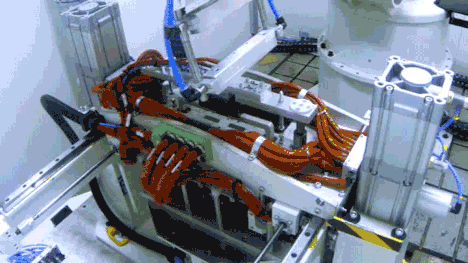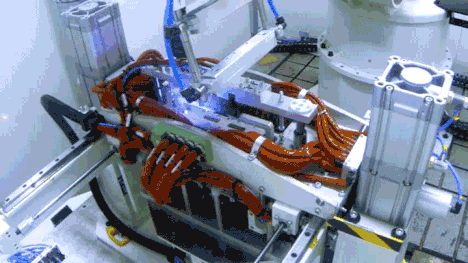
In the first half of 2025, the company invested RMB 10.095 billion in R&D, representing a 17.48% year-on-year increase, reflecting its strong emphasis on technological innovation and quality control.